Information Security, Cybersecurity and System Availability
Challenges and Commitments
Information technology has developed rapidly in the past years and plays a significant role in the business operations of organizations worldwide. This has resulted in cybersecurity threats being considered as a critical risk and challenge for global organizations.
Therefore, GGC is well aware of the risks relating to information technology and cyber security which present themselves in the forms of obstacles from external attacks on the IT system or internal leakage of personal and corporate data. Such risks can affect GGC’s operations and the safety of the personal data of employees, customers and suppliers. Therefore, GGC strives to develop a system that creates an IT shield through a secure governance structure and compliance with the Personal Data Protection Act as well as trainings to create confidence, knowledge and understanding for employees.
Key Stakeholders
Employee
Customer
Government
Supplier and Business Partner
Goals
of personal data, no complaints relating to cyber security incidents, and no employees or stakeholders fall victim to IT and cyber-attacks.
Management Approach
Cybersecurity Governance
GGC has established a policy for information technology security to be used as a guideline for the development of information security management systems and have a process of controlling the security of information technology systems according to standard ISO 27001: Information Security Management and Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies (COBIT). This covers the procedures regarding the use of information (Procedure) in order to manage operations for information and cyber securities, as well as to prevent and reduce risks and potential impacts.
The Structure of Overseeing Information and Cyber Security
In addition, GGC has established an information security and cyber security governance structure, which is regarded as the main process in building information security and protection against cyber threats. The working group is divided into 3 levels: Committee level, Management level, and Operation level.
| Governance Level | Role |
|---|---|
| Board Level Audit Committee |
|
| GC Group’ s Digital & IT Steering Committee (DISC) |
|
| ISMS Committee |
|
| Enterprise Architecture (EA Committee) |
|
| Chief Information Security Officer: CISO |
|
| Management Level |
|
| Operation Level |
|
Mitigation Actions for Cyber Threats and Information Leaks
Independent External Audit of the IT Infrastructure and/or information security management system inspections
GGC, in collaboration with its parent company GC, has conducted an assessment based on the ISO/IEC 27001:2013 standard to ensure that its Information Security Management System (ISMS) is both functional and aligned with international standards. The scope of the external audit includes Infrastructure as a Service, Infrastructure as a Service on Cloud, Internet Gateway Zone Management, and Application Management supporting the external recruitment process.
Information and Cyber Security Management Program
GGC has implemented measures to enhance Information and Cyber Security through the development of a security audit plan and the continuous improvement of information security technologies to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats. As part of this effort, GGC has developed a 5-year IT Action Plan covering the period from 2023 to 2027. Within this plan, Cybersecurity is identified as a key focus area with clearly defined actions.
The primary objective is to ensure that cybersecurity programs are regularly updated and maintained in alignment with best practices and international standards to effectively support GGC’s business goals and objectives. The Cybersecurity section of the IT Action Plan includes the following activities:
- Process and Infrastructure Assessment
- Enhanced system to close gap Vulnerability Assessment Scan
- Phishing Test & Tailor-made program for specific function
- Data Governance for GGC (Data Protection, Data Classification)
Process and Infrastructure
GGC has established an information security management system and asset security practices according to international standards and in compliance with cybersecurity practices. GGC also conducts annual inspections and reviews of the information and cyber infrastructure systems by external agencies. The past year’s review found that the process and infrastructure of GGC’s information and cyber systems meet international standards and do not have any defects.
As a subsidiary of GC, GGC has adopted GC’s Cyber Drill Procedure as a standard practice. This procedure serves as a comprehensive guideline for all IT personnel to follow, aiming to ensure effective and secure responses to incidents that may affect the company’s IT or cybersecurity systems. Additionally, it helps minimize potential damage from cybersecurity threats by providing clear preventive measures and response protocols. GGC conducts cyber drill procedure at least once during January–June and once again during July–December.
In addition, GGC has established an IT Security/Cybersecurity Disaster Recovery Plan, which outlines procedures to be followed in the event of a disaster affecting the primary data center. The purpose of this plan is to minimize potential damage and disruption to the organization. The plan provides detailed working procedures that serve as essential guidelines for all IT personnel in executing the Disaster Recovery Plan. It also outlines the expected recovery times for different types of IT information and the steps required to resume normal business operations. As part of the Security/Cybersecurity Disaster Recovery Process, GGC conducts incident response exercises and testing at least once during January–June and once again during July–December.
Vulnerability Assessment
GGC conducts a third-party vulnerability analysis at least twice a year. The company implements a Business Continuity Plan. In 2024, GGC conducted its annual Cyber Incident Response Tabletop Exercise to test the stability of data security and information technology systems. A simulated scenario of a Cyber Attack was created by an external intrusion, who tries to penetrate GGC’s IT Security in order to gather company’s, leading to company data leakage. Each VA (Vulnerability Assessment) will include the following key areas for review.
- Clickjacking
- Cookies Not Marked as Http Only
- Cookies with missing, inconsistent or contradictory properties
- Programming Error Messages
- Version Disclosure
- Content Security Policy Misconfiguration
- Permissions-Policy header not implemented
GGC inspects internal and external computer system vulnerabilities every 6 months in order to prepare a plan for protection and remediation from threats. GGC’s vulnerability severity levels are categorized into three levels: High Severity, Medium Severity and Low Severity.
Information Security and Cybersecurity Awareness
The Company raises awareness and prepares employees regarding cybersecurity at all levels through the knowledge testing, understanding and aware of e-mail-based threats (Phishing Test) and 3 E-Learning Cyber Security Online lessons, with an understanding assessment through a post-test at the end of the lesson. Employees can apply the knowledge gained in their work.
| 1. AI in Cybersecurity |
 By integrating AI tools into training programs, organizations can better prepare their workforce to navigate complex security challenges and build a more resilient digital defense system. |
| 2. Cybersecurity Third Party Risk Management. |
 This training focuses on ensuring that third parties meet security standards, comply with regulations, and refrain from introduce vulnerabilities into the organization’s cybersecurity system. Effective cybersecurity third party risk management helps safeguard sensitive information and maintain business continuity in an increasingly interconnected digital landscape. |
| 3. 10 important skills for Cybersecurity in 2024 that employees should have |
 The training provides 10 relevant skills for all employees to monitor and identify the possible cybersecurity that could occur among day to day work. The training also introduces the responsibility for information security for all employees. |
| 4. Data Governance |
 Data Governance Training equips employees with the knowledge and tools to manage data effectively, ensuring it is accurate, consistent, secure, and used responsibly across the organization. The training covers key principles such as data ownership, quality, privacy, compliance, and lifecycle management. By establishing clear roles, policies, and practices, data governance training supports better decision-making, regulatory compliance, and trust in organizational data. |
| 5. Cyber Vision |
 GGC has conducted the Cyber Vision for executives training. The training covers current technology trends, with this year’s focus on AI technology. Specifically, it will address cyberattacks driven by AI, aiming to equip employees with the knowledge and skills to effectively respond to various forms of cyber threats. |
| 6. Digital Thailand 2024 |
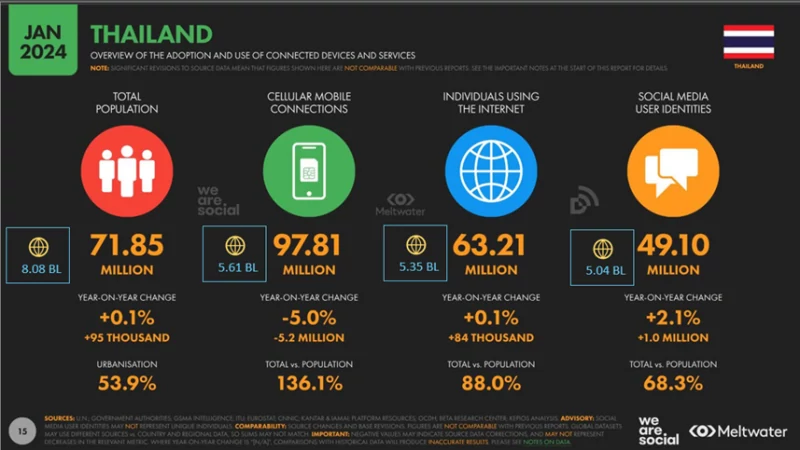 GGC has conducted the Digital Thailand for executives training. The training enhances knowledge on the trends in digital device and service usage in Thailand, providing in-depth insights into comparative analysis, internet users growth tracking in Thailand and resource accessibility in Thailand and in comparison with global platform. |
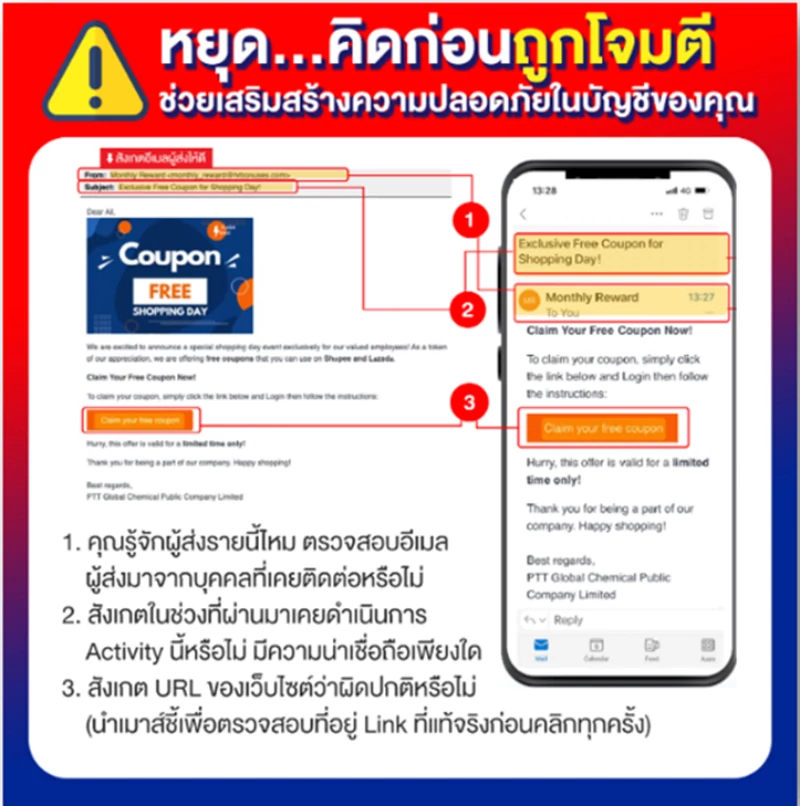
Phishing Reporting Process and Phishing Test in 2024
GGC has established the reporting of incidents, vulnerability or suspicious activities including the phishing email reporting. The suspicious activities reporting process begins when users or employees encounter the incidents. The response is carried out according to the process outlined below.
Employee Report on the phishing email
- A user encounters a phishing email and reports it to the service Desk
SOC Team Investigates the Incident
- Service Desk escalates the report to the SOC Team
- SOC Team determines the severity level: Low severity & High Severity (Escalate to SOC Manager and TF-IT Security team)
SOC Team Coordinates Mitigation
- SOC Team establishes the mitigation plan.
- SOC Manager notifies the Communication Team that phishing activity has occurred.
TF-IT Security Monitor Outcome
- After mitigation is complete, TF-IT evaluates results and confirms system stability.
SOC + TF-IT Construct Final Report
- Once back to normal, SOC and TF-IT Security Teams prepare a report.
- The Communication Team informs the organization that the issue has been resolved.
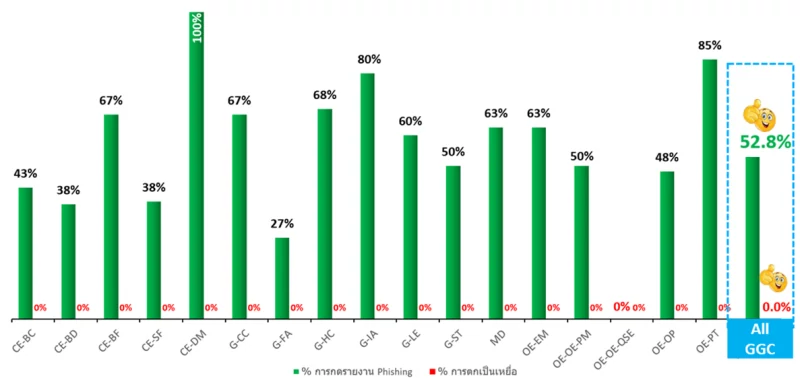
In 2024, it was found that out of a total of 282 employees who participated in the test, 217 employees passed, accounting for 77.2% of all participants . Additionally, 0 employees fell victim to phishing email, constituting 0 percent of the total. When compared to the previous test, the number of employees accurately reporting phishing incidents increased from 49 in 2023 to 52.8 percent in 2024.